Autoimmunity
Summary
Your body’s immune system protects you from disease and infection. But if you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake. Autoimmune diseases can affect many parts of the body.
No one is sure what causes autoimmune diseases. They do tend to run in families. Women - particularly African-American, Hispanic-American, and Native-American women - have a higher risk for some autoimmune diseases.
There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases, and some have similar symptoms. This makes it hard for your health care provider to know if you really have one of these diseases, and if so, which one. Getting a diagnosis can be frustrating and stressful. Often, the first symptoms are fatigue, muscle aches and a low fever. The classic sign of an autoimmune disease is inflammation, which can cause redness, heat, pain and swelling.
The diseases may also have flare-ups, when they get worse, and remissions, when symptoms get better or disappear. Treatment depends on the disease, but in most cases one important goal is to reduce inflammation. Sometimes doctors prescribe corticosteroids or other drugs that reduce your immune response.
A person may have more than one autoimmune disorder at the same time.
Diseases
Addison’s disease
Celiac disease - sprue (gluten-sensitive enteropathy)
Celiac disease is a condition caused by damage to the lining of the small intestine. This damage comes from a reaction to eating gluten. This is a substance that is found in wheat, rye, barley, and possibly oats. It is also found in food made from these ingredients.
Causes
The exact cause of celiac disease is not known. The lining of the intestines have small areas called villi which project outward into the opening of the intestine. These structures help absorb nutrients.
When people with celiac disease eat foods with gluten, their immune system reacts by damaging the villi. Because of the damage, the villi are unable to properly absorb iron, vitamins, and other nutrients. This may cause a number of symptoms and other health problems.
People with celiac disease are more likely to have:
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Sjogren syndrome
- Addison disease
- Down syndrome
- Intestinal cancer
- Intestinal lymphoma
- Lactose intolerance
- Thyroid disease
-
Type 1 diabetes
- Gut permeability to lactulose and mannitol differs in treated Crohn’s disease and celiac disease patients and healthy subjects - Nov 2008
Abstract
The gut barrier monitors and protects the gastrointestinal tract from challenges such as microorganisms, toxins and proteins that could act as antigens. There is evidence that gut barrier dysfunction may act as a primary disease mechanism in intestinal disorders. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the barrier function towards sugars after the appropriate treatment of celiac disease and Crohn’s disease patients and compare the results with those obtained with healthy subjects. Fifteen healthy volunteers, 22 celiac disease patients after 1 year of a gluten-free diet, and 31 Crohn’s disease patients in remission were submitted to an intestinal permeability test with 6.0 g lactulose and 3.0 g mannitol. Six-hour urinary lactulose excretion in Crohn’s disease patients was significantly higher than in both celiac disease patients (0.42 vs 0.15%) and healthy controls (0.42 vs 0.07%). Urinary lactulose excretion was significantly higher in celiac disease patients than in healthy controls (0.15 vs 0.07%). Urinary mannitol excretion in Crohn’s disease patients was the same as healthy controls (21 vs 21%) and these values were significantly higher than in celiac disease patients (10.9%). The lactulose/mannitol ratio was significantly higher in Crohn’s disease patients in comparison to celiac disease patients (0.021 vs 0.013) and healthy controls (0.021 vs 0.003) and this ratio was also significantly higher in celiac disease patients compared to healthy controls (0.013 vs 0.003). In spite of treatment, differences in sugar permeability were observed in both disease groups. These differences in the behavior of the sugar probes probably reflect different mechanisms for the alterations of intestinal permeability.
- Small-Intestinal Histopathology and Mortality Risk in Celiac Disease - Sep 2009
- What No One Is Saying About Zonulin — Is Celiac About More Than Genes and Gluten? Masterjohn - April 2011
- Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: Effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Drago - Apr 2006
Dermatomyositis
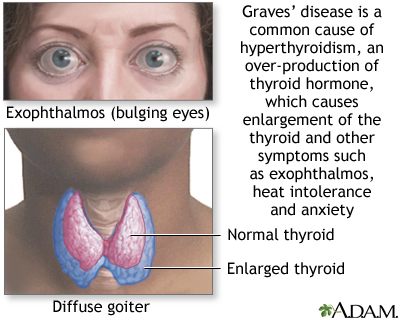
Graves’ disease
Graves disease is an autoimmune disorder that involves overactivity of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). Hallmarks of the condition are bulging eyes (exophthalmos), heat intolerance, increased energy, difficulty sleeping, diarrhea, and anxiety.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Chronic thyroiditis is caused by a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland. It often results in reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism).
The disorder is also called Hashimoto’s disease.
The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just above where your collarbones meet in the middle.
Causes
Hashimoto disease is a common thyroid gland disorder. It can occur at any age, but is most often seen in middle-aged women. It is caused by a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland.
The disease begins slowly. It may take months or even years for the condition to be detected and for thyroid hormone levels to become lower than normal. Hashimoto disease is most common in people with a family history of thyroid disease.
Multiple sclerosis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also affect other organs.
Causes
The cause of RA is not known. It is an autoimmune disease. This means the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
- LIPID PARADOX IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: THE IMPACT OF SERUM LIPID MEASURES AND SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION ON THE RISK OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE - Myasoedova - March 2011
Objectives
To examine the impact of systemic inflammation and serum lipids on cardiovascular disease (CVD) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
In a population-based RA incident cohort (1987 ACR criteria first met between 1988 and 2007), we collected serum lipid measures, erythrocyte sedimentation rates (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) measures and cardiovascular events including ischemic heart disease, and heart failure. Cox models were used to examine the association of lipids and inflammation with the risk of CVD and mortality adjusting for age, sex and year of RA incidence.
Results
The study included 651 RA patients (mean age 55.8 years, 69% female); 67% were rheumatoid factor positive. ESR was associated with the risk of CVD (hazard ratio [HR] 1.2 per 10 mm/hr increase, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.1, 1.3). Similar findings, although not statistically significant, were seen with CRP (p=0.07). We found a significant nonlinear association for total cholesterol (TCh) on risk of CVD, with 3.3-fold increased risk for TCh<4 mmol/L (95%CI 1.5, 7.2) and no increased risk of CVD for TCh≥4 mmol/L (p=0.57). Low low-density cholesterol (LDL<2 mmol/L) was associated with marginally increased risk of CVD (p=0.10); there was no increased risk for LDL≥2 mmol/L (p=0.76).
Conclusion
Inflammatory measures (particularly, ESR) are significantly associated with the risk of CVD in RA. Lipids may have paradoxical associations with the risk of CVD in RA, whereby lower TCh and LDL levels are associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation, lipid paradox, cardiovascular outcomes, ESR, CRP, lipids
- Dietary causes of rheumatoid arthritis - Obscure Science Nov 2018
Sjögren syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Type I diabetes
Symptoms
Symptoms will vary, based on the type and location of the faulty immune response. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- General ill feeling (malaise)
- Joint pain
- Rash
- Exams and Tests
- The health care provider will do a physical exam. Signs depend on the type of disease.
Tests that may be done to diagnose an autoimmune disorder include:
- Antinuclear antibody tests
- Autoantibody tests
- CBC
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Urinalysis
- Treatment
- The goals of treatment are to:
Treatment
- Control the autoimmune process
- Maintain the body’s ability to fight disease
Treatments will depend on your disease and symptoms. Types of treatments include:
- Supplements to replace a substance that the body lacks, such as thyroid hormone, vitamin * B12, or insulin, due to the autoimmune disease
- Blood transfusions if blood is affected
- Physical therapy to help with movement if the bones, joints, or muscles are affected
Many people take medicines to reduce the immune system’s abnormal response. These are often called immunosuppressive medicines. Examples include corticosteroids (such as prednisone) and nonsteroid drugs such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate, sirolimus, or tacrolimus. Targeted drugs such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers and Interleukin inhibitors can be used for some diseases.
Crohn’s Disease
Paleomedicina
- https://www.paleomedicina.com/en/blog/2015/11/crohns-disease-and-the-paleolithic-ketogenic-diet-a-graduation-thesis
- https://www.paleomedicina.com/hu/crohns-disease-successfully-treated-with-the-paleolithic-ketogenic-diet
-
ABSTRACT
Introduction: Crohn’s disease is regarded as having no curative treatment. Previous reports on dietary therapy of Crohn’s disease indicate no major success. Case Report: Here we report a severe case of Crohn’s disease where we successfully applied the paleolithic ketogenic diet. Dietary therapy resulted in resolution of symptoms, normalized laboratory parameters as well as gradual normalization of bowel inflammation as evidenced by imaging data and normalization of intestinal permeability as shown by the polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) challenge test. The patient was able to discontinue medication within two weeks. Currently, he is on the diet for 15 months and is free of symptoms as well as side effects. Conclusion: We conclude that the paleolithic ketogenic diet was feasible, effective and safe in the present case. Keywords: Crohn’s disease, Dietary therapy, In-flammatory bowel disease, Ketogenic diet, Paleo-lithic diet
INTRODUCTION Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory disease of the bowel, is regarded as having no cure [1]. Standard treatment which involves steroids, immunosuppressants and biological therapy is aimed at reducing symptoms [1]. Periods of flares and remissions typically alternate, however, the overall course of the disease is progressive. A set of ecological evidence, including a discrepancy between westernized and non-westernized countries in the occurrence of the disease, raises the possibility of lifestyle and/or dietary factors in the etiology of the disease [2]. There have been several attempts to use a dietary intervention in Crohn’s disease such as the specific carbohydrate diet [3] and the anti-inflammatory diet [4] as well as elimination-reintroduction diets [5]. Although clinical improvements and reduction of medicines have been reported being associated with these diets we are not aware of any diet inducing complete remission and long-term freedom of medicines at the same time.The authors of the present report are using a diet referred to as the paleolithic ketogenic diet in the treatment of chronic conditions. So far we have published cases of successful treatment of diabetes type 1 [6, 7] and type 2 [8], epilepsy [9, 10] as well as other conditions [11].
CASE REPORT
Diagnosis
The 14-year-old boy presented with fatigue, low grade fever, iron deficiency anemia, lower abdominal tenderness and perianal dermatitis. He was of short stature for his age. On 30 September 2013 upper and lower endoscopy was performed. The latter showed ulcerative lesion in the terminal ileum. Biopsy was taken from multiple sites and histopathology showed severe inflammation of the terminal ileum and the Bauhin’s valve. Signs of mild-to-moderate degree aspecific inflammation were seen in the colon. On laboratory workup inflammatory marker C reactive protein (CRP) was elevated (58 mg/L). He was diagnosed with Crohn’s disease.
Standard treatment
At the time of diagnosis onset (on 07 October 2013) the patient was started on mesalazine, metronidazole and pantoprazole. Within ten days, ciprofloxacin and probiotics were added. Given that no improvement was seen immunosuppressant therapy was initiated on 13 November 2013 with azathioprine together with methylprednisolone, potassium citrate, calcium and vitamin D. Given that disease progressed, a year after diagnosis onset (on 25 September 2014), biological therapy was initiated: five cycles of adalimumab were given each two weeks apart. The condition of the patient further deteriorated and therefore on 07 November 2014 exclusive formula feeding was initiated. At this time mesalazine, multivitamin, vitamin D3 and calcium were discontinued. Pantoprazole was discontinued within two weeks. Formula-based nutrition resulted in the resolution of abdominal pain but other symptoms persisted (Table 1, Figures 1 and 2).
Laboratory data
As the disease progressed iron deficiency anemia of the patient worsened. Thrombocyte number showed a decreasing tendency across the course of the standard treatment. Level of inflammatory markers CRP and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) dropped when initiating the immunosuppressant therapy and steroid but increased thereafter (Table 1, Figure 2).ImagingAt the time of the diagnosis ultrasound examination performed on 07 October 2013 showed thickening of the terminal ileum and that of the small intestine at multiple sites. No thickening of the colon was seen. Three further follow-up ultrasound examinations were carried out during the next year. This showed progression of the disease as reflected by increasing diameter of the thickened bowel wall and an increasing intensity of hypervascularization. The last ultrasound out of the four (on 7 November 2014) already indicated the thickening of nearly all bowel segments including the colon ascendens and the colon transversum. Figure 3 shows as the largest diameter of the terminal ileum changed between 7 October 2013 and 7 November 2014.
Magnetic Resonance Enterography
Magnetic resonance enterography performed five weeks after diagnosis onset (on 12 November 2013) indicated thickening of the small intestinal wall at multiple locations. A follow-up magnetic resonance enterography 13 months later, on 16 December 2014, showed an increase in the variability in the diameter of the bowel lumen and narrowing of the lumen (Figure 4). Due to the narrowing the patient was offered surgery in December 2014 which he refused. SymptomsAbdominal cramps as well as episodes of low grade fever lessened when initiating the immunosuppressant therapy together with steroid. However, within three months the patient developed bilateral knee pain as a new symptom. Later on his appetite deteriorated. At 12 months after diagnosis onset abdominal cramps increased and episodes of low grade fever returned. The patient reported fatigue along with a deterioration in his school performance. Following the onset of the biological therapy all symptoms persisted. Following the fourth cycle of adalimumab strong abdominal pain emerged abruptly which persisted for several hours. Given this experience and the overall ineffectiveness of the biological therapy the patient decided to stop it. He was put on exclusive enteral nutrition which resulted in a lessening of his abdominal cramps but other symptoms persisted.Dietary advices while on the standard therapyThe patient was advised to follow a diet free of lactose and low in fat and fibers. Analysis of his diet-symptom diary did not show any consistent association between symptoms and food items.
Intervention with the paleolithic ketogenic diet
Given the ineffectiveness of standard therapies the parents of the child were seeking for alternative options. When we first met the patient he reported bilateral pain and swelling of the knee, frequent episodes of fever and night sweats as well as fatigue. He looked pale. We offered the paleolithic ketogenic diet along with close monitoring of the patient. The patient started the diet on 4 January 2015. The diet is consisting of animal fat, meat, offal and eggs with an approximate 2:1 fat : protein ratio. Red and fat meats instead of poultry as well as regular intake of organ meats from pork and cattle were encouraged. Grains, milk, dairy, refined sugars, vegetable oils, oilseeds, nightshades and artificial sweeteners were excluded. Small amount of honey was allowed for sweetening. The patient was not taking any supplements. Regular home monitoring of urinary ketones indicated sustained ketosis. Regular laboratory follow-up was used to monitor the course of the disease as well as for giving feedback how to fine tune the diet. The patient was under our close control and gave frequent feedbacks and so we could assess the level of dietary compliance. The patient maintained a high level dietary adherence on the long-term, yet on his birthday, he made a mistake: he has eaten two pieces of commercially available “paleo” cake which contained coconut oil, flour from oilseeds as well as sugar alcohol. Clinical consequences are discussed later. From July 2015 onwards he also consumed small amounts of vegetables and fruits. Given the persistence of certain alterations in laboratory values (mild anemia) on 10 November 2015, despite 10 months on the paleolithic ketogenic diet, we suggested to tighten the diet again. From this time on he did neither consume vegetables and fruits nor vegetable oil containing spices such as cumin and cinnamon.We obtained written informed consent from the patient for the publication of his case.
RESULTS
Discontinuing medication
Within two weeks after diet onset the patient discontinued azathioprine, the only medicine he was taking at this time. Currently, he is without medicines for 15 months. SymptomsThe frequent night sweats of the patient disappeared within three weeks after diet onset and thus his sleep improved significantly. The knee pains of the patient began to lessen at 4th week on the diet and completely disappeared by the third month. From this time onwords he regularly went to school by bike (20 km daily). He reported restored energy and increased physical and mental fitness. Although during the eight months before diet onset his weight was declining, following diet onset he began to gain weight. At diet onset his weight was 41 kg and was 152 cm tall (BMI = 17.7). At 12 months after diet onset, his height was 160 cm and weighted 50 kg (BMI: 19.5). The change in his height and weight is depicted in Figure 5. At the time of writing the article he is on the diet for 15 months and is free of symptoms as well as side effects.Laboratory workupLaboratory workup including blood and urinary analysis was performed seven times during follow-up. Urinary ketones were positive on each occasion. Blood glucose was between 5 and 5.4 mmol/l. Renal and liver function as well as ions were normal. His severe iron deficiency anemia was reversed already on the fourth week of the diet: iron level increased from 3.6 μmol/L to 12.1 μmol/L. Inflammatory markers including ESR and CRP decreased significantly: at four weeks CRP was 3.75 mg/L while ESR was 3 mm/h (Figure 2). Thereafter inflammatory markers elevated to some extent. Thrombocyte number was already low before diet onset but decreased further following diet onset. The last laboratory follow-up, however, on 14 December 2015, indicated an increase in thrombocyte number (Table 2.).
Imaging
Ultrasound examination of the abdomen was carried out five times during follow-up and was performed by the same investigator. The first examination following the onset of the paleolithic ketogenic diet, on 29 January 2015, showed significant improvement. Although wall of the terminal ileum was still thickened hypervascularization was no longer present. Thickening was still seen in the coecum and the ileum but not in the other regions which were described as being affected on the preceding ultrasound examination. A follow-up exam on 09 April 2015 showed further improvement: thickening of the wall of the terminal ileum decreased and no abnormal was seen in any other regions. A next ultrasound which was made following eating the “paleo cakes” showed thickening of the wall of the terminal ileum to as much as 6 mm. On the next examination, on 19 Jun 2015, thickening of the terminal ileum decreased to 4.5 cm. Three months later, on 17 September 2015, the examination showed no abnormality (Figures 2 and 3).
Intestinal permeability test
Intestinal permeability was assessed using a polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) challenge test based on the method of Chadwick et al. [12]. PEG 400 contains a mixture of inert water soluble molecules of 11 different sizes that are absorbed independently of dose, but which display decreasing mucosal transport with increasing molecular size. PEG 400 is also nontoxic, not degraded by intestinal bacteria, not metabolized by tissues, and rapidly excreted in urine. After a 3.0-gram oral dose of PEG, the subject makes a six-hour urine collection. The PEG fractions are acetylated with acetic anhydride, using pyridine as a catalyst, and then quantitated by capillary gas-liquid chromatography. The percentage of each fraction of PEG excreted over 6 hours is calculated.PEG 400 challenge test performed at four months on the diet (on 18 May 2015) showed increased permeability to PEG between 242 and 418 molecular weight. A follow-up test performed at 10 months on the diet (on 26 November 2015) showed no abnormal intestinal permeability (Figure 6).
DISCUSSION
Here we report a case where Crohn’s disease was reversed by the paleolithic ketogenic diet. Disease symptoms began to improve a few weeks after diet onset. Within 10 months the patient achieved full remission from symptoms as well as normalization of intestinal inflammation as evidenced by imaging data, normalization of laboratory parameters and that of the intestinal permeability. Aside from a single dietary fault the patient strictly adhered to the diet as assessed by frequent patient feedback, laboratory data and home monitoring of urinary ketones. Given the patient’s severe condition upon the first visit the paleolithic ketogenic diet was started in the strictest form thus containing no vegetables and fruits at all. Such a diet may first sound restrictive but our previous experience indicate that a full fat-meat diet is needed in the most severe cases of Crohn’s disease. In addition, our experience shows that even a single occasion of deviation from diet rules may result in lasting relapse. This was the case in the present patient too where breaking the strict rules (eating the ”paleo cakes”) resulted in a thickening of the bowel wall. Based on our experience this is due to the components of the popular paleolithic diet including coconut oil, oil seeds and sugar alcohols which may trigger inflammation. In contrast, honey, consumed in limited amounts is tolerable and does not cause such symptoms. The significant improvement seen in the last laboratory exam also indicates that the paleolithic ketogenic diet is most effective when containing no plant components at all.Crohn’s disease is known to be characterized by a progressive worsening of symptoms. Standard therapies may result in a temporary symptom relief but are accompanied by significant side effects [1]. Surgical resection is thought to be inevitable on the long-term [13]. Our patient also failed to respond to immunosuppressive therapies, steroid, biological agents and exclusive formula feeding. Within 14 months after diagnosis onset, he was offered surgery due to the narrowing of the bowel. The paleolithic ketogenic diet reversed the disease from this very advanced stage. Although Crohn’s disease is known to be characterized by an alternation of better and worse periods, a complete remission from a very advanced stage is highly unlikely to be the part of the normal course of the disease. While on the biological therapy thrombocyte number dropped and continued to decrease while on the diet. Our previous experience does not indicate thrombocytopenia on the paleolithic ketogenic diet. However, low thrombocyte number is a well-known side effect of the use of adalimumab in Crohn’s disease [14, 15]. It is also noteworthy that a return to the strictest form of the paleolithic ketogenic diet resulted in an increase in thrombocyte number.Crohn’s disease is regarded as an autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases and Crohn’s disease specifically have been linked to increased intestinal permeability [16]. Yet currently there is no known means to reverse pathological intestinal permeability [17]. A previous study with the paleolithic diet found no change in intestinal permeability as assessed by the lactulose-mannitol test [18]. As far as we know this is the first documented case where pathological intestinal permeability was reversed as assessed by a diagnostic test.Experts in the field of evolutionary medicine has long been suggesting that chronic diseases of civilization emerge from a mismatch between our ancient genome and current lifestyles [19, 20]. In recent years an increasing number of studies showed that the metabolic syndrome and associated conditions can be reversed or improved by applying a diet denoted as ”paleolithic” (for a review see: [21]). In the paleolithic diet, as described in the implied papers, macronutrient ratios are undefined or variable, as well as that of the ratio of animal/plant foods including the ratio of animal/plant fats. Our clinical experience, however, indicate that the most severe chronic conditions, including the Crohn’s disease, can only be reversed by the paleolithic ketogenic diet based on animal fat, meat and offal. A same conclusion was drawn in our previous case study showing that the paleolithic ketogenic diet was more effective than the popular form of the paleolithic diet in the case of Gilbert’s syndrome [11]. The paleolithic ketogenic diet we use in the treatment of chronic diseases is close to the evolutionary diet originally proposed by gastroenterologist Voegtlin [22]. With regard to the main principals, background, sustainability and further issues such as vitamin supply while on a meat-fat based diet we refer to the excellent book of Voegtlin [22].As regards the underlying mechanism, we put forward that normalizing pathological intestinal permeability is crucial in tackling autoimmune diseases, including Crohn’s disease. Accordingly, increased intestinal permeability has been shown to predict relapses in Crohn’s disease [23]. It is known that under physiological conditions, dietary macromolecules are not transported paracellularly from the intestinal lumen to the blood or the lymph. It has been suggested that certain components of the Western-type diet are able to destroy cell junctions and thereby compromise the intestinal barrier function [24, 25]. As a result, large molecules including protein fragments and glycoproteins, possessing antigenic properties, may appear in the circulation and promote chronic inflammation [26]. Given their specific structure, these macromolecules may bind to and form complexes with the surface molecules of certain cell types. Such a complex is then destroyed by the immune system through apoptosis [27, 28]. We assume that a continued exposition to these macromolecules may maintain the autoimmune destruction of tissues. We put forward that the animal fat-meat based diet, the only diet humans are evolutionary adapted to, is lacking substances that are destroying the intestinal barrier. A shift toward the paleolithic ketogenic diet may normalize intestinal permeability (as also seen in our patient) and thereby may halt the autoimmune destruction of the affected tissues, in our case the intestine. With the attenuation of the autoimmune process the intestine may regenerate.
CONCLUSION
We conclude that the paleolithic ketogenic diet was effective while producing no side effects in this case of Crohn’s disease. In contrast to standard therapeutic approaches which are aimed to control certain components of the disease only, the paleolithic ketogenic diet was able to reverse the cluster of symptoms and abnormalities associated with the disease. Assuming a long term dietary compliance, we believe that the patient would remain disease-free in the future